 music |
 | OSdata.com |
Boolean AND
summary
This subchapter looks at Boolean AND.
free computer programming text book projecttable of contents
|
 music |
 | OSdata.com |
This subchapter looks at Boolean AND.
free computer programming text book projecttable of contents
|
This subchapter is a stub section. It will be filled in with instructional material later. For now it serves the purpose of a place holder for the order of instruction.
Professors are invited to give feedback on both the proposed contents and the propsed order of this text book. Send commentary to Milo, PO Box 1361, Tustin, California, 92781, USA.
This subchapter looks at Boolean AND.
Please note the differences between a logical Boolean operation, an integer Boolean operation, and a bit-wise Boolean operation. Note that terminology varies, so you will eventually see references using these terms different than presented here.
In the case of a logical Boolean AND, the result is a logical BOOLEAN type of either TRUE or FALSE. Some languages, such as C, do not have a built-in Boolean type. There are several different and incompatible encodings for TRUE and FALSE (see table below).
In the case of an integer Boolean AND, the AND is performed on the two integers as whole numbers. The result can be inaccurate if the integer is not in a specified form (the legal options usually being [ZERO and ONE] or [ZERO and NEGATIVE ONE]. This works best with -1 and 0 as TURE and FALSE (or vice versa). There are several different and incompatible encodings for TRUE and FALSE (see table below).
| some languages | TRUE | FALSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 1 | 0 | ||
| C | non-zero | zero | ||
| negative | zero or positive | |||
| -1 | 0 | |||
| 0 | 1 |
in the case of a bit-wise Boolean AND, a logical AND is performed on each corresponding bit of the two bit strings (or two single bits).
AND requires both objects to be true for the result to be true. The AND works like a pair of switches in series. Both switches must be closed for current to flow.
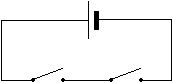
AND is conisdered to be Boolean multiplication and is represented by the middle dot symbol: · (such as A·B). As in ordinary algebra, AND (Boolean multiplication) can be written by dropping the middle dot (such as AB). There is no Boolean division operation.
The truth table for AND is as follows:
| A | B | result |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
The AND gate in logic circuits looks like:
![]()
The AND operation (Boolean multiplication) has the same results as ordinary arithmetic multiplication..
The AND operation has a result of 0 when any of its input variables is 0.
The AND operation has a result of 1 only when both of its input variables are 1.
Most programming languages use the AND operator in conditional expressions to test if two parts of the conditional expression are both true.
BASIC AND — BASIC operator used in the IF-THEN statements as a logical operator.
Some languages allow the use of the AND operator to return a numeric value.
BASIC AND — Optional BASIC operator used in as a logical operator returning a numeric value. If the AND condition is met, a -1 is returned. If the AND condition fails, then a 0 is returned. Example: PRINT A=15 AND B=33
Some languages allow the use of the AND operator as a bit wise binary operator.
BASIC AND — Optional BASIC operator used in as a bit wise bianry operator.
Some languages have an AND function.
APL AND ∧(x) — APL dyadic function that returns the logical AND of two scalars, vectors, or matrices. Form is A∧B. This function can be used with two arrays, vectors, or matrices to logically AND all of the corresponding elements of the two arrays, vectors, or matrices; or with an array, matrix, or vector and a scalar to logically AND the scalar to every element of the array, vector, or matrix with the value of the scalar; or with two scalars to logically AND the two scalars. Each element of the operation must intiially have the value of one (1) or zero (0). One is TRUE and zero is FALSE.
BASIC AND — Wang BASIC 2200B function. Form is AND(p$,q$) or AND(p$,q). In the first form, the two string variables are bit-wise ANDed on a character by character basis. In the second form, the two-digit hexadecimal constant is bit-wise ANDed with each character in the character string P$.
LISP AND(x) — LISP predicate function that takes zero or more arguments of type NIL or nonNIL and returns either NIL or nonNIL. Arguments are evalutaed left to right. Evaluation stops at the first NIL and remaining arguments are not evaluated, returning NIL. If NIL is not encountered, then the function returns the value of the last argument.
Coding example: I am making heavily documented and explained open source code for a method to play music for free — almost any song, no subscription fees, no download costs, no advertisements, all completely legal. This is done by building a front-end to YouTube (which checks the copyright permissions for you).
View music player in action: www.musicinpublic.com/.
Create your own copy from the original source code/ (presented for learning programming).
return to table of contents
free downloadable college text book
Because I no longer have the computer and software to make PDFs, the book is available as an HTML file, which you can convert into a PDF.
| previous page | next page |
| Tweets by @osdata |
free computer programming text book projectBuilding a free downloadable text book on computer programming for university, college, community college, and high school classes in computer programming. If you like the idea of this project, Supporting the entire project: If you have a business or organization that can support the entire cost of this project, please contact Pr Ntr Kmt (my church) free downloadable college text book on computer programming. |
This web site handcrafted on Macintosh ![]() computers using Tom Bender’s Tex-Edit Plus
computers using Tom Bender’s Tex-Edit Plus ![]() and served using FreeBSD
and served using FreeBSD ![]() .
.
†UNIX used as a generic term unless specifically used as a trademark (such as in the phrase “UNIX certified”). UNIX is a registered trademark in the United States and other countries, licensed exclusively through X/Open Company Ltd.
Names and logos of various OSs are trademarks of their respective owners.
Copyright © 2010 Milo
Created: December 5, 2010
Last Updated: December 14, 2010
return to table of contents
free downloadable college text book
| previous page | next page |